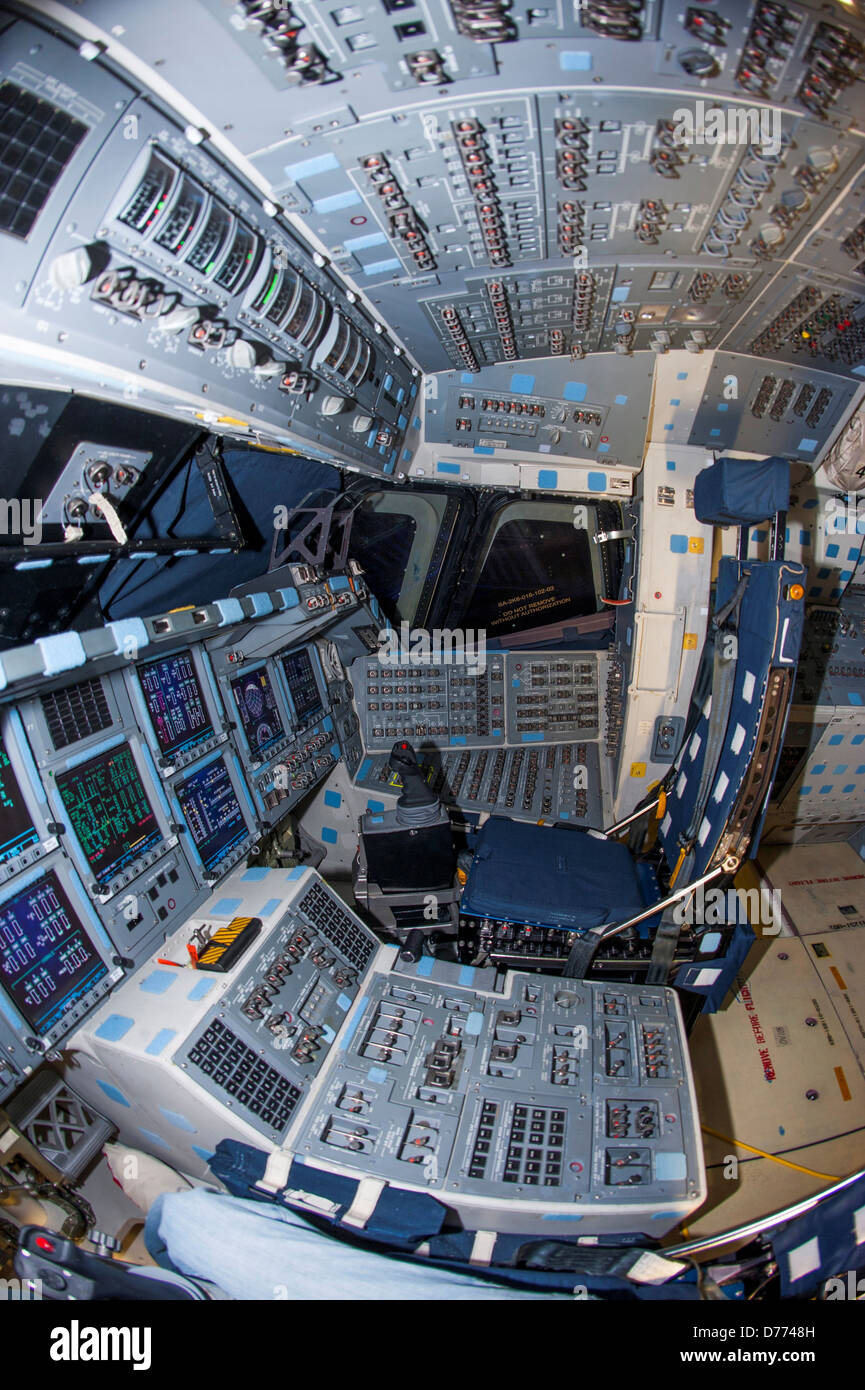


Like the Space Shuttles, the Buran vehicles had engines located at the back, and two wings for a controlled landing back on Earth.ĭevelopment of the programme began in 1976, with the reusable spacecraft (although the booster was not) capable of performing operations in orbit before returning to Earth.īut after the one unmanned spaceflight in 1988, the programme was scrapped following the dissolution of the USSR in 1993. Astronaut Robert Cabana narrates the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 to the International Space Station.Shuttlesource is a space shuttle video a. The Buran shuttle was intended to be launched on the huge Energia booster, similar to the giant booster rockets used by the Space Shuttle orbiters. The stars of the project, called the Buran program, were its.
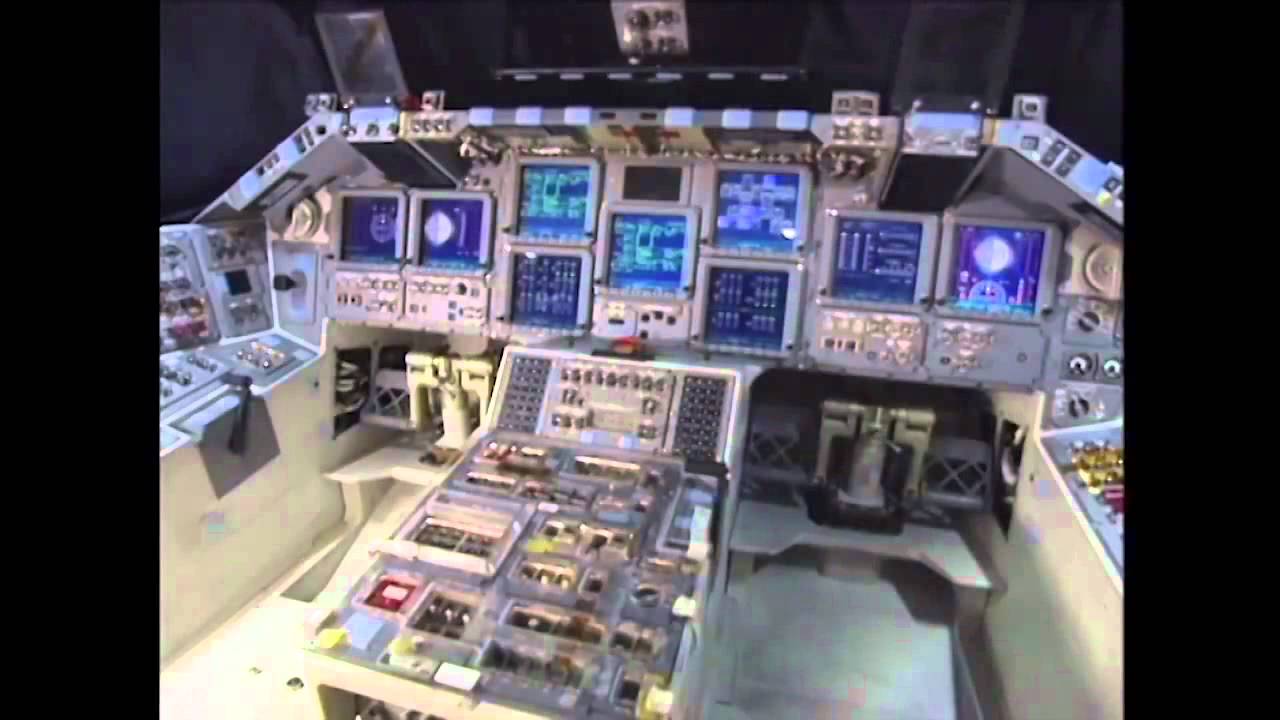
Their similarity in appearance to Nasa’s Space Shuttles is not accidental - at the time, this was deemed to be the best way to create a vehicle that could travel to and from orbit, although some have also suggested espionage was at play. In 1974, Russia launched its largest, most expensive project in space exploration history. Only five spaceplanes have successfully flown to space, re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and safely landed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
